
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wind Turbine FAQThis article was
taken from the
Rainbow Power Company
The Power of WindAir moving at 40 Kph through one square meter theoretically has an energy content of 400 watts if it were stopped. The power extracted from the wind cannot exceed 59% of the power in the wind. Wind Variations
Whereas with Solar or Hydro-electric power the batteries
receive some recharge on a daily basis, at times there
may not be any significant wind for charging the
batteries for weeks on end. Winds are notoriously
variable, and most installations must include an
auxiliary generating system to recharge the batteries in
low wind periods.
Planetary Winds
Planetary wind systems, normally called prevailing
winds, are those great moving air masses that
dominate whole areas and show constant directional
characteristics, varying only with the movement of
high or low pressure systems and with the seasons of
the year. Local Winds
Local winds, by contrast, are caused by temperature
differences created by local topographic conditions.
Site Evaluation
In order to know if a wind powered system is either
feasible or cost competitive you need to have some
facts and figures. Because of the site preparation
and work that needs to go into a wind tower, you
need to have done all of your home-work before you
take the big step.
A Simple Evaluation MethodA very simple method of measuring the strength of the wind can be carried out as follows. You need 30 cm of thin fishing line (or similar), a table tennis ball, a protractor, and a spirit level. You fix the ball to the end of the fishing line, and fix the other end of the fishing line to the centre of the protractor. When the wind blows the ball moves and the angle of the line changes. By reading the angle on the protractor and using the chart below you can estimate the strength of the wind. The spirit level is used to make sure that the top edge of the protractor is horizontal. 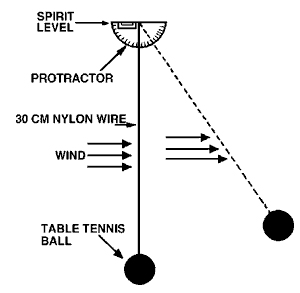 Measuring the Wind
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Getting Results
Sampling the wind variations over a period of a few
weeks will not necessarily give an indication of the
yearly wind cycle. Since most people don't want to
twiddle their thumbs for a year while taking
readings, then approximate schemes must be found.
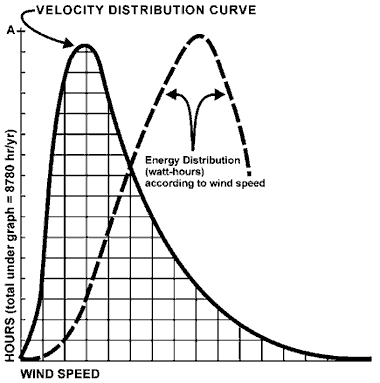
The chart is called the velocity distribution curve.
It is a similar shape for all wind power locations,
and gives a good indication of amount of time the
wind blows at a particular wind speed.
Wind Velocity and Rotor Diameter
The power from the wind increases as a function of the
cube (third power) of the wind velocity. Increasing the
diameter of the rotor increases the power output as a
square function. Power from the wind can be derived by
the formula: 
The furling wind speed is the amount of wind required to
produce the maximum power that the generator is capable
of; any wind in excess of this will not generate more
than this maximum.
Choosing the Correct Tower HeightThe two most important considerations in planning the tower height for a wind turbine are avoidance of turbulent air flow produced near ground level by the 'roughness' of the terrain over which the wind flows, and avoidance of excessive ground drag which lowers wind velocity near the ground and severely restricts the performance of a wind turbine. TurbulenceA wind turbine must never be located such that it is subject to excessively turbulent air flow. Light turbulence will decrease performance since a turbine cannot react to rapid changes in wind direction, while heavy turbulence may reduce expected equipment life or result in wind turbine failure. You can detect turbulence by streaming a long ribbon from a guyed pole or mast to see if it streams easily in high winds from various directions. The mast should be roughly as high as you would envisage the wind tower to be. Turbulence may be avoided by
following a few basic rules: 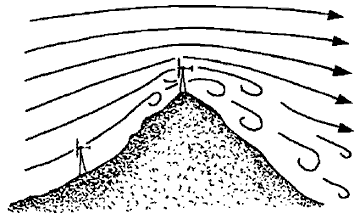
High, rough hilltops may produce
substantial turbulence in the windstream. Tower number 1 is located on the
relatively gentle smooth lower slope and will be clear of most turbulence when
the windstream is left to right in the drawing, but will be in the wind shadow
of the hill when the wind reverses.

The grove of trees in this example will produce turbulence. A higher tower close to the trees places the wind generator above the turbulence. A shorter tower is safe if placed far enough away from the trees. 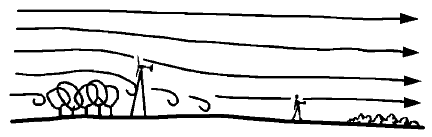
Severe turbulence may be created by the sea cliff in this example. As above, a higher tower will be required near the cliff while a shorter tower will be safe if placed at a great enough distance from the cliff. 
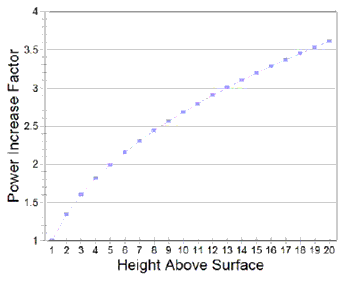
Ground DragThe avoidance of ground drag will
increase performance dramatically. Up to a considerable height, the least
expensive way to increase your power output from a wind turbine is to increase
tower height.

As an example in the use of this curve, if a
windspeed of 15 kph were measured at 2 metres above
the surface, the windspeed at 20 metres height can
be predicted from the curve.
Tower Construction
The smaller wind generators (up to 100 watts) can be mounted on a sturdy pipe
with guy wires. The larger machines would need a more substantial tower in which
case it is advisable to contract a person experienced in the erection of wind
generator towers. SafetyDo not place a wind-plant in a turbulent area, to avoid severe stress on wind turbine components and tower. All the controls, necessary safety (governing and feathering) devices to protect against excessively high wind speeds, instruction manual etc should come with the machine that you purchase. What may not be provided is a suitable regulator to prevent your battery from being overcharged. The Kite TestA sturdy kite with crepe paper or thin cloth ribbons or strips can give a good indication of variable air turbulence of site under different wind conditions. 
The Effect of Obstacles A wind turbine needs to be sited away from the turbulent air flow, preferably upwind or a long way down wind (considering prevailing wind direction). Otherwise you may need a very high tower. 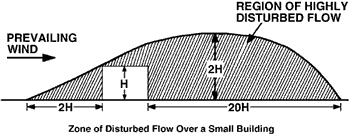
NoiseWind generators may produce a fair amount of noise, particularly in high winds. Beyond a couple of hundred metres, the noise of the wind itself generally drowns out the noise of the wind generator. Australian Wind AssessmentHigh wind areas are often associated
with coastlines. 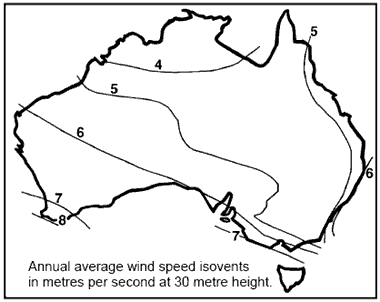
Wind Speed Conversion Factors
Visualising Wind TurbulenceWind turbulence can be visualised by studying a small fast flowing stream with obstacles such as rocks and boulders. The wind follows the same flow patterns. 
Rainbow Power Company Ltd is an unlisted public company, incorporated in 1987 to design, manufacture, sell and install renewable energy equipment based on solar, wind, hydro and biomass energy sources. To learn more about their services please visit their site http://www.rpc.com.au |



